The Top 10 OSHA Violations for 2020

The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has announced its preliminary Top 10 most frequently cited workplace safety standards for fiscal year 2020.
Although multiple standards swapped positions, the top 10 violations from FY 2019 to FY 2020 did not change.
Ladders (1926.1053) climbed to a top-five spot, and Respiratory Protection (1910.134) rose to the third rank from fifth. Additionally, the data show that Fall Protection – General Requirements (1926.501) is OSHA’s most frequently cited standard for the 10th successive fiscal year.
The top 10 for FY 2020 are:
- Fall Protection – 5,424
- Hazard Communications – 3,199
- Respiratory Protection – 2,649
- Scaffolding – 2,538
- Ladders – 2,538
- Lockout/Tagout – 2,065
- Powered Industrial Trucks – 1,932
- Fall Protection – Training – 1,621
- Eye and Face Protection – 1,369
- Machine Guarding 1,313
Upcoming Events
EHS Today: OSHA Inspections –How to Handle It – and Prevent It
- April 13
- 1-hour live webinar to help understand OSHA Inspections
KEEP AN EYE OUT FOR THE DATE OF OUR NEXT HAZWOPER REFRESHER COURSE COMING UP IN MAY! RESPIRATOR FIT-TESTING TO BE OFFERED AT THE EVENT!
Pre-Startup Safety Review – The Forgotten Element
Pre-Startup Safety Reviews (PSSR) are among the most overlooked and/or forgotten steps in Process Safety Management. These reviews should be done before introducing a covered process chemical into any piece of equipment or system, and are the last chance to discover something that may have been overlooked. The reviews consist of several dozen generic questions (e.g. has Process Safety Information been updated? or has a Process Hazard Analysis been completed?). The PSSR affords much latitude and there is nothing in the statutes that keeps us from customizing the review to be more equipment specific. In addition to the generic questions referred to above, consider additional equipment specific questions such as:
- Initial Startup Procedure developed?
- Normal Operation Procedure developed?
- Startup After Turnaround or Emergency Procedure developed?
- Emergency Operations Procedure developed?
- Temporary Operations Procedure developed?
- Normal Shutdown Procedure developed?
- Emergency Shutdown Procedure developed?
- Pumpout and Isolation Procedure developed?
- Technical operating specification information developed?
- Included in Material and Energy Balance Calculation?
- Included in Maximum Intended Inventory Calculation?
- Plugs, caps or blind flanges installed on service and drain valves?
- International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration (IIAR) Ammonia Refrigeration Safety Inspection Checklists developed? (Ammonia Processes ONLY)
- Preventative maintenance (PM) schedules developed?
- PM schedules uploaded to Computerized Maintenance Management Software?
- Lockout / Tagout Procedure developed?

If the previous listed or similar questions are required to be answered for every piece of equipment the PSSR is conducted on, then there is less of a risk of overlooking something that could result in a release.
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs)
P&IDs are used throughout the industry to show the relationships between equipment and instrumentation in the system. They can also show other information to enhance clarity, such as how ammonia flows through the system. P&IDs are part of PSI, and while there are many variations of these diagrams, their purpose is the same as other diagrams in the system and plays a critical role in assisting operators to perform their duties.
The layout of P&IDs is not standardized throughout the industry – engineers are free to document their designs in any way the customer sees fit.
P&IDs must include at least the following:
- Process Equipment with Identification
- Process piping, sizes, identification, and direction of flow
- Valves
- Control Valves
- Relief Valves
- Instruments
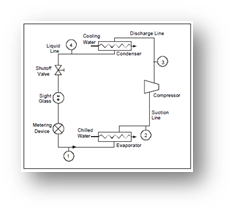
P&IDs are developed during the system’s design stage and updated with as-built drawings. It is critical system owners/operators review them regularly to ensure accuracy. P&IDs also require updating to reflect any changes made to the system.
Verify their accuracy and that all requirements are contained within. P&IDs are as important as the system itself.


0 Comments